Losing weight with the gastric balloon
Obesity is a real public health problem in France, with 17% of the national population concerned.
It leads to psycho-social consequences (functional gene in daily life, social discrimination, etc.), and especially medical complications, which not only reduce life expectancy, but also impair its quality:
- metabolic complications
- cardiovascular complications
- digestive complications
- respiratory complications
- rheumatologic complications
Obesity is a factor in increasing the risk of cancer.
The different techniques
Bariatric surgery offers various interventions such as gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy, or Bypass to patients with morbid obesity.
But in recent years, new techniques, non-surgical, are now available to patients with moderate and severe obesity who are not eligible for obesity surgery.
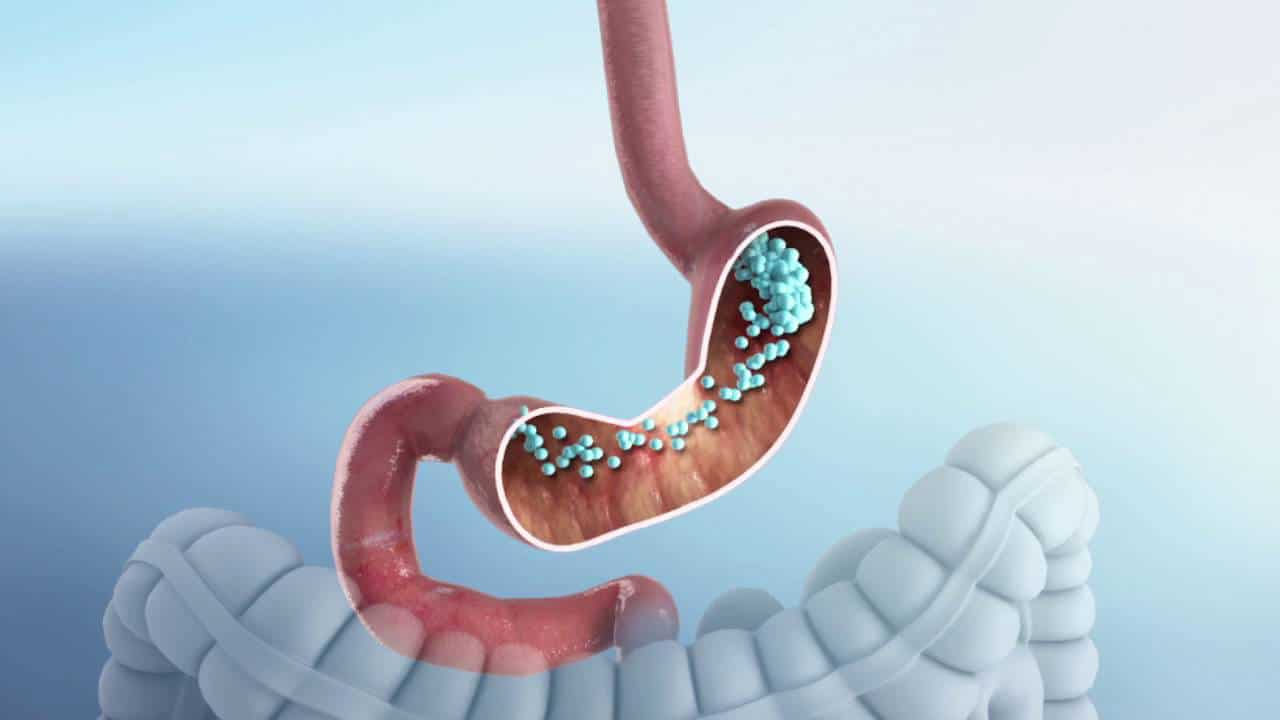
Gastric balloons slow down the emptying of food in the stomach, which reduces the feeling of hunger, increases satiety and reduces daily energy intake.
Scientific studies have shown that the gastric balloon causes weight loss and improved co-morbidities related to obesity.
The average weight loss observed at balloon removal at 6 months is 15 kg (range: 0-25 kg), or 12% of body weight. The loss of excess weight is 32% and the BMI falls by five points.
Health Insurance does not support device, installation and removal.
Several types of gastric balloons
Several types of balloons are marketed with a duration of 4 months (Elipse®), 6 months (BIB®, Heliosphère®Newtech®,Endball®) and 1 year (Orbera 365®, Spatz®).
Some are inflated with a liquid and others with air or a mixture of liquid and air.
The gastric balloon is indicated in combination with a multidisciplinary management (nutritional, behavioral and physical coaching)
- in overweight or non-morbidly obese patients (BMI> 27 kg/m2 depending on the type of balloon) who could not achieve sustained weight loss despite nutritional management by a doctor or nutritionist
- in patients with morbid obesity (BMI> 40 or> 35 kg/m2 with comorbidities) who refuse bariatric surgery
- in super-obese patients (BMI> 50 kg/m2) before bariatric surgery
There are contraindications that will be eliminated during the assessment before the installation of the balloon by the doctor.

The installation of the gastric balloon
The pose is most often preceded by fibroscopy of the stomach to verify the absence of pre-existing pathology that may contraindicate the establishment of the device. This examination also allows to put the balloons except the unmanageable balloons.
Balloons are often placed as outpatients by gastroenterologists trained in this technique, but hospitalization may be necessary in case of poor tolerance.
After placing a gastric balloon
A treatment is prescribed to reduce the possible side effects the days following the installation of the balloon due to the adaptation of the stomach to the balloon.
Nutritional and behavioral management after removal of the balloon is imperative for medium-term effectiveness.
Common side effects are observed immediately after the balloon is placed: abdominal pain and vomiting. They are most often prevented by the medical treatment prescribed by the gastroenterologist.
Complications are rare but can be severe. Patients should contact the medical team for the duration of the balloon placement in case of pain and / or vomiting at a distance from the balloon.
In conclusion
The gastric balloon is an endoscopic technique for the management of overweight and obesity when combined with nutritional and behavioral management and the resumption of regular physical activity.
Sources :
- ESTEBAN study 2015
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, N Engl J Med 20162.Genco A, Cipriano M, Bacci V, Maselli R, Paone E, Lorenzo M, et al.Intragastricballoonfollowed by diet vs. intragastricballoonfollowed by anotherballoon: a prospective study on 100 patients. ObesSurg 2010 Nov; 20 (11): 1496-500.
- Genco A, Balducci S, Bacci V, Materia A, Cipriano M, Baglio G, et al.Intragastricballoon or dietalone? A retrospectiveevaluation. ObesSurg 2008 Aug; 18 (8): 989-92.
- s-Vliegen EMH, Tytgat GNJ. Intragastricballoon for treatment-resistantobesity: safety, tolerance, and efficacy of 1-year ballo-controlled by a 1-year balloon-free follow-up. GastrointestEndosc 2005 Jan; 61 (1): 19-27.
- Dumonceau J-M. Evidence-basedreview of the Bioentericsintragastricballoon for weightloss. ObesSurg 2008 Dec; 18 (12): 1611-7.